Your New Intranet Starts Here
Streamline communication, boost collaboration, and empower your team with MyHub's intuitive intranet solution.
Book a live demo now and experience the difference.
Take a Quick TourHave you ever lost a veteran employee and suddenly realized there’s a massive knowledge gap? It happens more often than you think. Whether due to retirement or resignation, critical expertise is walking out the door every day. The impact is real: according to recent Forbes stats, 10,000 Baby Boomers retire daily. And the Great Resignation isn’t slowing down – nearly half of workers plan to leave their jobs soon.
No matter the reason, failing to capture and retain organizational knowledge has serious consequences. Productivity, innovation, and performance all suffer. In today’s fast-paced world, knowledge transfer isn’t a luxury – it’s a necessity for companies that want to stay ahead of the curve.
How To Transfer Knowledge
We understand how difficult it can be to prioritize knowledge management when your to-do list is already overflowing. That’s why we’ve created a simple six-step framework to help you establish an effective knowledge transfer process. Plus, we provide ready-to-use knowledge transfer templates to help you hit the ground running.
In this in-depth guide to knowledge transfer, we explore key topics such as:
- Definition of knowledge transfer and why it matters
- Key benefits of implementing knowledge transfer in your organization
- The hidden costs of knowledge loss
- Different types of organizational knowledge you should capture
- Common barriers to knowledge sharing and how to overcome them
- Best practices and principles for knowledge management
- How to develop a strategic knowledge transfer plan
What Is Knowledge Management?
In today’s workplace, there’s more data, information, and insight than ever before. Organizing, sharing, and using it effectively has become a major challenge. So, what is knowledge management?
It’s the process of structuring, storing, and distributing information in a way that aligns with your business goals.
With the explosion of digital tools and cloud storage, companies must take a strategic approach to managing both internal and external knowledge sources. Knowledge management systems ensure that employees have access to the right information at the right time – improving collaboration, productivity, and decision-making.
Organizations that embrace a strategic knowledge management approach are more adaptable, innovative, and efficient. But the key is alignment: collecting data is not enough. You must connect insights to real workplace application – transforming data into actionable knowledge that drives results.
What Is Knowledge Transfer?
Knowledge transfer is the process of moving essential information, skills, and experience from one part of your organization to another. It ensures that your team can retain and apply expertise, even when employees leave or move into new roles.
It’s not just about documents and systems. On-the-job learning through mentoring, shadowing, and collaboration plays a vital role. Effective knowledge transfer means capturing what’s in people’s heads and making it available in a centralized, searchable format for everyone.
What Are the Benefits of Knowledge Management to an Organization?
Effective knowledge management supports organizational development, drives efficiency, and boosts employee engagement. Here are the top benefits:
- Safeguard Against Knowledge Loss: A strategy based on a structured knowledge transfer plan template minimizes disruption when employees leave. With a central knowledge base, everyone, whether remote or in-office, can access institutional knowledge instantly.
- Encourage Continuous Improvement: Knowledge sharing fosters a culture of ongoing learning and development. Employees are more likely to upskill and collaborate when knowledge flows freely across teams.
- Boost Productivity: With less time wasted searching for answers or reinventing the wheel, teams can focus on high-impact tasks. Knowledge sharing reduces errors, increases agility, and supports better resource allocation.
- Enhance Innovation & Decision-Making: When people have access to relevant expertise, they make better decisions faster. Knowledge transfer empowers teams to solve problems creatively and deliver higher-quality outcomes.
- Speed Up Onboarding: A comprehensive, well-documented knowledge repository helps new hires ramp up quickly. It reduces reliance on formal training and accelerates time-to-productivity.
Costs To Organizations Of Not Transferring Knowledge
The bottom line is that failing to transfer knowledge costs organizations money, often a substantial amount. That’s the key takeaway from research by Panopto.
Effective knowledge transfer can result in significant savings. For small businesses, it may save up to $2 million annually in employee productivity. For larger enterprises, the potential savings can soar to $200 million, thanks to reduced downtime and more efficient onboarding processes.
What Are The Types Of Knowledge Transfer?
Two primary types of knowledge must be captured and transferred effectively in any business:
- Explicit knowledge
- Tacit knowledge
Explicit Knowledge
Explicit knowledge is formal and easy to document. It includes information found in training manuals, SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures), company databases, and how-to guides. For example, setting up a new supplier in your procurement system is an explicit process that can be recorded and easily shared with others.
Tacit Knowledge
Tacit knowledge is much more nuanced and challenging to capture. It consists of personal experience, intuition, judgment, and insights gained through years on the job. An example in the workplace might be recognizing when a potential client is primed for a sales pitch–a skill honed over time and difficult to write down. Unfortunately, it’s often this kind of deep, experiential knowledge that walks out the door unnoticed when employees leave.
What Are The Barriers To An Effective Knowledge Transfer Process?
Before implementing a robust knowledge transfer plan, it’s essential to understand the most common barriers to knowledge sharing.
One major issue is that experts may underestimate the value of what they know. Their experience becomes second nature, and they may not recognize what others need to learn. As a result, essential knowledge remains undocumented and eventually disappears.
Another problem is the lack of standardization. Without a clear, repeatable process for capturing and sharing insights, knowledge transfer becomes inefficient and inconsistent. Both the giver and the recipient of the knowledge can become overwhelmed without a guiding structure.
Communication gaps can also hinder the process. Just because someone is a subject-matter expert doesn’t mean they can easily explain their workflow. That’s where clear formats and templates become invaluable.
And finally, diverse learning styles within the workforce pose another challenge. Employees vary widely in their preferences–some may favor visual content, while others prefer step-by-step text. Generational differences and comfort with technology further complicate knowledge transfer efforts.
Knowledge Sharing: Guiding Principles
Here are some essential best practices for effective knowledge sharing in your organization:
- Foster organizational buy-in: Ensure leadership and teams across the business support and engage with the knowledge transfer process.
- Clarify ownership: Make it clear that company knowledge is a shared asset, not something owned by individuals.
- Promote trust and transparency: Create a culture of open communication using regular team meetings, whether virtual or in-person, to build rapport.
- Embrace diversity: Design your knowledge management system to accommodate different learning preferences and tech literacy levels.
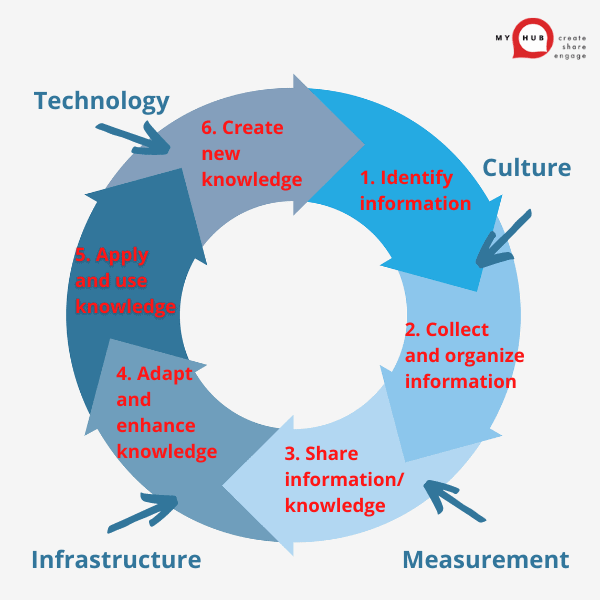
How To Transfer Knowledge In Six Simple Steps
1. Identify The Knowledge To Transfer
The first step is to pinpoint critical knowledge–both what needs to be shared and who needs to receive it. Ask yourself: If key personnel left tomorrow, what know-how would leave with them? This includes both explicit processes and invaluable tacit insights.
Encourage internal experts to help identify gaps and share what they know. Use discussions, surveys, or interviews to understand which roles are most at risk and which knowledge is essential for business continuity.
- What roles pose the highest risk for knowledge loss?
- What do these individuals know that others don’t?
- Which information is mission-critical?
- How does the team manage when key people are unavailable?
- Is this information currently documented or shared?
2. Collect Knowledge
Gathering knowledge isn’t about dumping information into a database. It’s about structured collection using consistent formats. A standardized process saves time and ensures completeness. Our free knowledge transfer checklist simplifies this step by identifying what’s important and how to document it effectively.
Ask staff to use the provided template to record their workflows, tips, and nuances. This approach ensures knowledge is captured in a reusable and coherent format that benefits everyone in the organization.
Free Knowledge Transfer Checklist Template
Use the following customizable template to document critical tasks and processes. This tool allows you to capture knowledge not only about individual roles but also about cross-functional tasks, skills, and repeatable workflows.
Remember, your approach should reflect your organization’s size and capacity. Choose the method, interviews, videos, or documentation, that best suits your environment. Refer to earlier examples in this guide for inspiration and adapt accordingly.
Our Knowledge Transfer Checklist is available as a Word document or PDF download.
Knowledge Transfer Checklist – Word format
Knowledge Transfer Checklist – PDF format
| Name | Job role/area of expertise/process/task/skill | Knowledge transfer method |
| Overview | A brief overview of the context and the knowledge transfer being conveyed. | |
| Objectives & responsibilities | A summary of the jobholder’s overall objectives and responsibilities or the task, process, or skill. | |
| Deliverables | For a jobholder, this includes detailed information on work in progress and a status report for all projects.
For a task or process, describe the required outputs and the milestones towards their achievement. |
|
| Contacts | A complete list of internal and external contacts required for the completion of the jobholder’s duties or to achieve the task or process. | |
| Meetings | A schedule of meetings relevant to the jobholder’s duties or completing the task, plus a database of minutes and agendas. | |
| Compliance & regulatory requirements | Details of any central or local regulations and compliance requirements. | |
| Budgetary & financial | Information on any budgetary or financial parameters within which the jobholder or task operates. Details on how budgets are set and reporting responsibilities are assigned. | |
| Risks | Details of any risks associated with the jobholder’s duties or the task, including their management and mitigation. | |
| Tacit knowledge | A record of the jobholder’s insights, accumulated wisdom, and knowledge.
Concerning a task or process, information on what works well and why, plus any acquired expertise about execution. |
3. Share Knowledge
This step focuses on delivering the right information to the right people in the most effective format. Several methods are available for doing so, and the key is to make sharing knowledge simple and meaningful for both the sender and the receiver.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to knowledge sharing. Organizations must tailor their strategies to meet specific business goals and accommodate various employee learning styles.
Here are proven tools and methods for sharing explicit knowledge – the kind that can be documented, written down, and widely distributed:
- Expert blogs that explain processes or reflect thought leadership
- How-to videos with visual demonstrations
- Collaborative wikis for living documentation
- Live or recorded webinars for real-time learning
- Educational conferences that expand professional knowledge
- Informative podcasts shared internally or publicly
- Engaging infographics and diagrams
- Detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- Intranet-based FAQs for easy reference
And here are suggested formats for transferring tacit knowledge – the hands-on experience and personal insight that can’t be easily documented:
- Mentoring and coaching programs
- Work shadowing sessions
- Interactive simulations and gamification
- Structured coaching engagements
- Internal communities of practice
- Peer-led collaborative learning groups
- Formal apprenticeships or internships
All collected knowledge should be organized in a centralized, searchable knowledge base. This system should serve as the single source of truth for your organization. To encourage ongoing communication, consider integrating tools like business instant messaging platforms that keep your workforce connected.
Lastly, ensure your system includes security and privacy protocols to protect your most valuable intellectual property (IP) and confidential information.
4. Adapt and Update Knowledge
Knowledge management is an ongoing process, not a one-time activity. Your team will constantly develop new skills, insights, and best practices. Encourage this growth by establishing a system that continually captures, reviews, and updates knowledge.
Create a rolling plan that includes structured check-ins, audits, and contributions. Assign responsibility for content upkeep and ensure outdated knowledge is regularly replaced with current, accurate information.
5. Apply Knowledge
Once your knowledge transfer system is in place, it’s time to put it to work. Make sure employees are not only accessing knowledge but also applying it effectively in their roles.
Set measurable success indicators that reflect improvements in efficiency and quality. For instance, if the shared knowledge focused on boosting sales follow-up, look for a measurable increase in conversion rates or engagement along the sales funnel.
6. Create New Knowledge
In an age of constant change, your organization must be ready to innovate. As new technologies, tools, and insights emerge, your knowledge strategy should evolve too.
Repeat the knowledge transfer cycle – from identification to application – to ensure your organization stays agile and competitive. This continual refinement ensures your teams remain aligned with evolving business goals and challenges.
Knowledge Transfer Main Takeaways
Knowledge transfer is the process through which experienced employees share their insights, workflows, and lessons learned with others across the organization. It bridges the gap between individual expertise and collective capability.
A well-executed knowledge transfer strategy protects your business from knowledge loss when key personnel depart. It also boosts productivity, minimizes costly mistakes, and fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
To make the process less daunting, break it into the following actionable steps:
- Identify company-critical knowledge that must be preserved
- Standardize the process with a reusable template or framework
- Diversify sharing methods to suit different learning styles
- Review and refine your process regularly for relevance and accuracy
- Encourage real-world application and measure impact
- Foster a culture of innovation by continuously generating new knowledge
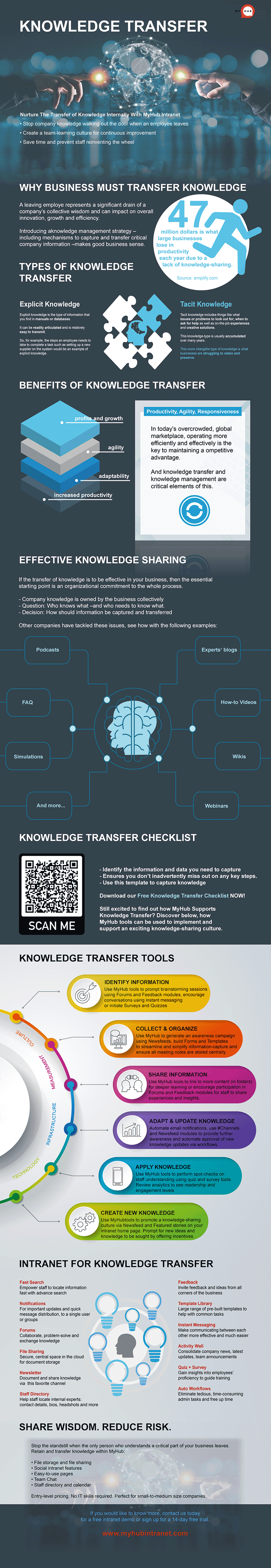
Knowledge Transfer Infographic
Need a quick and visual summary of the knowledge transfer process? Check out our knowledge transfer infographic that outlines all the essential steps in one easy-to-understand image. For enhanced clarity, you can also download a high-resolution version here:
knowledge-transfer.png
How MyHub Supports Knowledge Transfer
Discover how MyHub’s feature-rich intranet tools empower your organization to build a sustainable, collaborative, and efficient knowledge-sharing culture. Below is a brief overview of how to transfer knowledge successfully using our platform.
1. Identify Knowledge And Practical Skills
Begin by identifying key knowledge areas and skill gaps across your teams. Invite staff to highlight recurring challenges and suggest areas where insights could benefit others. This helps activate internal experts and encourages them to start formally documenting what they know.
Use MyHub’s Forums, Feedback, and Survey modules to spark brainstorming sessions and collect feedback. Leverage #Channels for real-time discussions, and enrich the Staff Directory with detailed employee bios to connect knowledge holders with learners.
2. Collect & Organize Multi-Format Knowledge
Encourage team members to document workflows and processes using clear formats, such as customizable “How To” templates. Assign key personnel to gather both explicit and tacit knowledge, and determine a consistent structure for storing it all.
Centralize information within a dedicated knowledge transfer hub that becomes your organization’s single source of truth. Utilize MyHub tools like Newsfeeds and the Latest Activity Wall to create awareness campaigns. Build Forms and Templates to capture insights efficiently and consistently.
3. Knowledge Transfer = Share Knowledge
Develop a consistent, reliable method for sharing knowledge. This can include creating virtual learning communities where employees can find, explore, and contribute insights.
Use MyHub’s #Channels and Newsfeeds for high-level updates that link to deeper content housed in folders. Foster collaboration through Forums and Feedback modules, encouraging staff to share experiences, discuss challenges, and co-develop solutions.
4. Adapt and Update Knowledge
Keep your content fresh and relevant by creating a continuous knowledge update cycle. Determine what each team member needs to know and how new information should be integrated into their workflow.
Automate alerts using email notifications to inform users when content is added or changed. Use #Channels, Newsfeeds, and workflow automation tools to track task progress, manage approvals, and maintain up-to-date documentation.
5. Apply Knowledge
To ignite knowledge transfer, you need to empower your teams to put their knowledge into action. Encourage cross-functional mentoring, work shadowing, and on-the-job training to ensure that what’s been shared is truly being applied.
Use MyHub’s survey and quiz modules to assess employee comprehension. Leverage analytics to measure content engagement, track readership, and identify which resources are most useful in day-to-day operations.
6. Create New Knowledge
Foster a culture of innovation by encouraging employees to keep learning and contributing fresh insights. This ensures your organization continues to evolve and remains competitive.
Repeat steps 1 through 5 to maintain a sustainable knowledge ecosystem. Promote knowledge creation via Newsfeed highlights, Featured Stories on your home page, and incentive-based idea challenges using MyHub tools.
Knowledge Transfer? MyHub!
Ready to implement a streamlined knowledge management strategy? MyHub’s powerful intranet software supports every stage of the process, from capturing knowledge to updating, applying, and sharing it across your organization.
All the tools you need for to transfer knowledge are available in one secure, user-friendly digital platform.
Start your journey with a free personalized demo or explore our 14-day trial to experience it firsthand.
FAQ Section
What is a knowledge transfer process?
It’s a structured method to capture, organize, share, and retain essential expertise—both documented and tacit—across an organization, ensuring continuity and reducing knowledge loss.
Why is knowledge transfer important?
It prevents critical know-how from disappearing when employees leave, boosts efficiency by reducing errors, supports compliance, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
How can MyHub support knowledge transfer?
MyHub’s intranet offers tools like forms/templates, document libraries, newsfeeds, workflows, forums, quizzes, and alerts to manage each step—from capture to application—smoothly and effectively.