Team Collaboration
How To Help Staff Connect, Encourage Ideas, And Move Work Forward
Share. Communicate. Innovate

Team collaboration is a prominent trait among today’s winning organizations. Done right, collaboration aids better decision-making, innovative thinking and improved productivity. Staff are happier, performance is boosted, and there’s less risk of error.
But many organizations have yet to figure out how to help colleagues work better together to achieve a common goal.
The good news is that there are tools and techniques that have proven to nurture a strong collaborative culture within the workplace.
Here, we shed light on the causes of poor collaboration, tips for improvement, and collaboration software that enables co-workers to share ideas and improve internal communications.
What Is Team Collaboration?
The definition of team collaboration is when two or more people work together to achieve a common goal. This is done through idea sharing, planning and executing in unison. In contrast to working on one’s own, team collaboration is regarded as a more productive way to get work done, and carries less risk.
Tackling a major project – such as a new product launch or the introduction of a new internal process – usually requires a teamwork approach. This entails bringing together a group of employees to allocate and complete tasks, within a set timeframe.
These days, with technology overcoming geographical barriers, virtual teams are popular. Companies are now appointing the best people for a project – regardless of their work location – to form part of a team and collaborate. This development has created new opportunities for businesses to innovate – but is not without its challenges.
Why Is Team Collaboration Critical In The 21st Century?

Never before has the workplace been so diverse. For the first time in history, five generations are working side-by-side. Each employee has a unique perspective. Their opinions are formed by their own personal experiences. And they have different communication styles – some prefer face-to-face, others the written word.
Such differences are a lot to manage, particularly when complex, project-based decisions must be made.
How a team interacts with each other will influence the final outcome. Communication, knowledge transfer and equal respect for each team member are essential for a high-performing team.
Younger generations joining the workforce are eager to further develop the collaborative skills they’ve learnt during education. They place place greater support on social tools for collaboration than their older colleagues (49 per cent millennials vs 31 per cent baby boomers). And considering that 46 per cent of 2020’s workforce are millennials (compared with 36 per cent six years ago), employers must act upon this growing generation’s preference for building team dynamics.
Furthermore, around 75% of employees now rate teamwork and collaboration as crucial to their performance.
Reasons For Poor Team Collaboration
It’s a common scenario when a collection of people come together to solve a problem, cross-functionally. There may be representatives in the room from IT, Sales, Product and Finance.
When collaboration fails, it’s often because these individuals partially listen to others points-of-view, but do not fully seek to understand what they were actually saying.
Each representative remains in their own paradigm rather than genuinely taking on board and seeking a solution based on other perspectives.
To counter this, effective collaboration requires recognition of diversity; that each individual has their own thought process and purpose. This requires greater understanding of the team individuals, and the concerns they may be feeling.
These could include the following:
- Skepticism about the success of the project i.e.‘doomed to fail’
- Uncertainty around who does what in the team, and where tasks and responsibilities sit
- Misinterpretation or miscommunication: wrongly assuming all staff have the same understanding
- Lack of direction, KPIs and milestones set out from the start
- Conflicting priorities: failing to appreciate an employee’s current workload before adding more
- Forcing staff to communicate in ways that may be uncomfortable for them i.e. introverted employees making team presentations
How To Improve Team Collaboration
Successful team collaboration is hard work. With so much to consider – silos, company culture, staff at different locations, leadership styles – good team collaboration doesn’t happen by accident.
Furthermore, Harvard Business Review has exposed an interesting paradox at play, based on its research into team behavior:
“Although teams that are large, virtual, diverse, and composed of highly educated specialists are increasingly crucial with challenging projects, those same four characteristics make it hard for teams to get anything done.
“To put it another way, the qualities required for success are the same qualities that undermine success. Members of complex teams are less likely to share knowledge freely, to learn from one another, to shift workloads flexibly to break up unexpected bottlenecks, to help one another complete jobs and meet deadlines, and to share resources.”
It also found that the higher the educational level of the team member, the more challenging collaboration appears for them.
But there are some best practices for building effective collaboration strategies, as follows:
Define And Repeatedly Communicate The Team’s Goals
This is the first step to bringing together a group of people. Goals should be reiterated at the start of daily huddles, referred to when key decisions are underway, and repeated across all communication channels (your intranet, for example).
Promote Open Communication Particularly When Faced With A Roadblock
This is where technology has become a game-changer. Instead of waiting for the next round-table meeting to overcome a roadblock, intranet tools such as forums, instant messaging, and shared files allow members of the same team to work through a problem collaboratively at pace.
Create Structure Within Meetings And Give Staff Time To Prepare
WIP (work-in-progress) meetings are an important part of effective project management. Ahead of each meeting, share agenda items, action lists and related reading material with all members of the team so there are no frustrating delays when teams meet.
Encourage Creativity And Free-thinking: All Ideas To Be Respected
Brainstorming sessions can be fun and fruitful. Team leaders must give advance warning though so staff can do their own research. And if you’re the manager, resist the urge to direct and jump in immediately with your ideas, as staff may feel obliged to follow.
Log Important Decisions And Their Backstory
Avoid the “he said/she said” nature of spontaneous conversations; make sure ideas are contextually documented in a central space, accessible for all, and not lost in the moment.
Invest in Collaboration Tools
Team collaboration tools have shown the way here. Employees can set up team channels where decisions can be made in real-time. Slack, the popular chat tool, has been joined by a host of other instant messaging tools, virtually eliminating the need for traditional email. Video conferencing, in the wake of Covid-19, has become the default meeting format. And forums are another effective channel for effective team collaboration.
Check For Understanding
Nodding heads does not necessarily mean agreement and understanding. Many co-workers won’t like to admit they don’t understand something. Reiterate major decisions – during and after meetings – providing clarity and an opportunity for others to ask further questions. Engage in two-way communication with all members when possible.
Create Ways For Less Outspoken Team Members To Contribute Ideas
Not everyone has public speaking skills. Shy people will not feel comfortable sharing their idea in a room full of colleagues, but may happily submit an idea via a forum or chat channel. Make it known that individual thinking is unique and valued, and that every team member should be able to communicate with equality and authority.
Share Experience, Knowledge And Resources
Use an intranet to capture treasured insights – physically and virtually with file-sharing software. This will save mistakes being repeated, and knowledge walking out the door when someone leaves. Don’t leave this to chance: embed a process for eliciting and storing this valuable intelligence as part of your regular WIP meetings. Add tags to meeting notes that can be searched for later on.
Acknowledge And Celebrate Individual And Team Success
Highlight individual qualities and the special skills that each team member brings to the table. Go big when a milestone or key task has been ticked off with a team building celebration event. This boosts morale and makes people feel valued.
Appoint Task And Relationship-Oriented Leaders
HBR research found that the most productive and innovative teams had leaders who could outline clear goals and responsibilities and easily switch to relationship-building mode i.e. smoothing out internal tensions.
Limit Group Sizes
Not always possible – particularly if you’re about to organize the next Olympics – but aim to keep teams small enough so that staff get to know (and respect) each other, and ideas exchange freely. Big teams tend to be more vulnerable to tunnel vision, or the ‘squeakiest wheel wins’.
❝
Collaborative teams are 5 x higher performing as they feel motivated towards a common goal
Source: i4cp
Team Collaboration Trends
Team Collaboration tools are evolving to suit the changing needs of businesses today.
Flexibility, scalability, and compatibility with existing systems increasingly matter. Because of this, enterprise players such as Cisco, Slack and Microsoft have no choice but to integrate with each other.
Some other noticeable trends in team collaboration include:
Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning tools and bots can help an entire team improve the way they collaborate by making it easier to find information instantly. They can also offer things like real-time translation and transcribing during video conferencing meetings.
Unique Experiences
As more technology vendors come to the integration and interoperability party, open-source platforms with the help of APIs are enabling employers to build their own collaboration experience, just right for their internal culture.
Love Of Video
This format’s popularity continues to rise, but so do expectations around its performance. With remote teams the new normal, businesses are relying more on video conferencing, which must be reliable, secure and consistent.
Team Collaboration Software
Creating a workplace using team collaboration software is a practical move that can really transform how you and your colleagues collaborate.
MyHub’s cloud-based intranet is designed specifically for organizations in search of an affordable and adaptable collaboration solution. It’s fully scalable, designed to support your company’s growth. And fully customizable, to meet your exact needs.
Combining a company internal newsfeed, instant messaging and secure cloud storage, MyHub is the perfect choice for your important projects-in-progress.
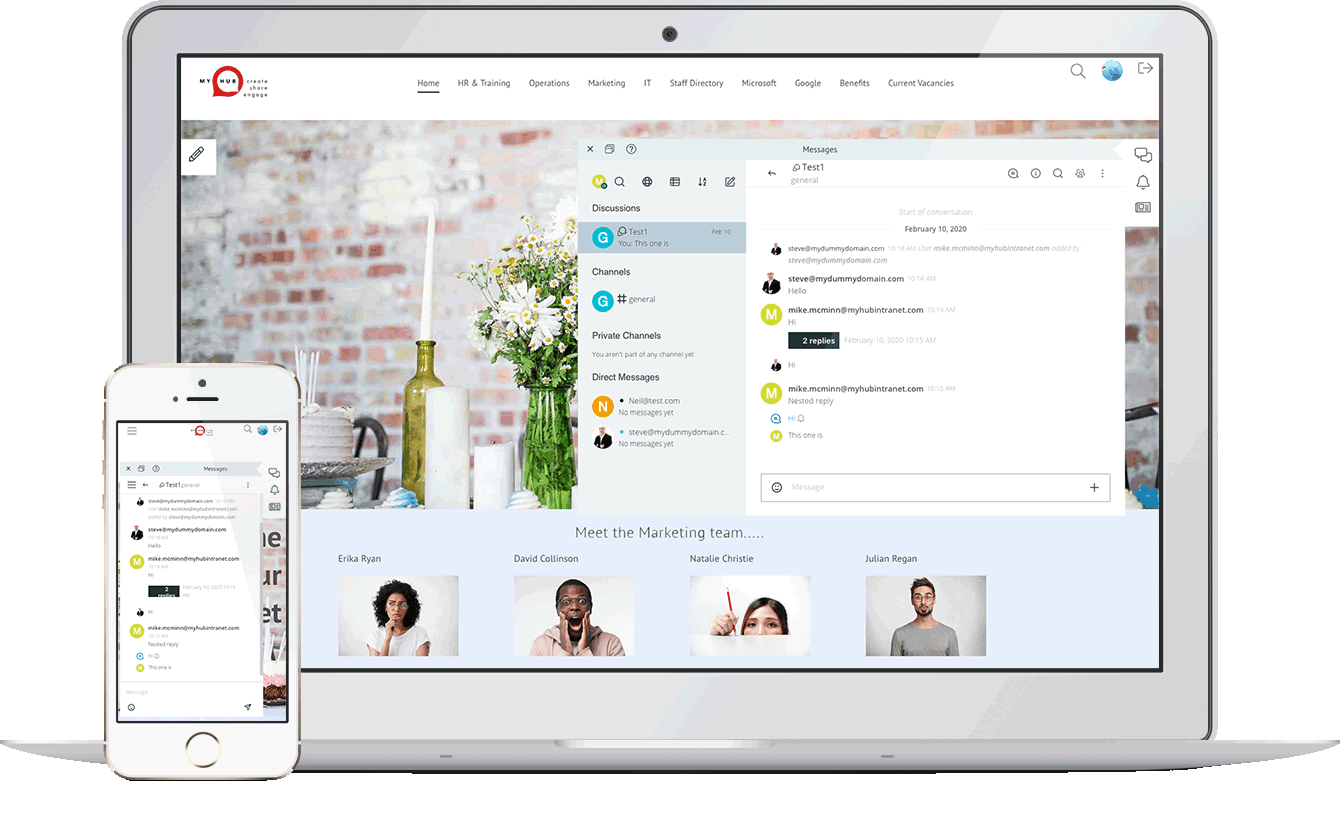
Whether you’re an IT pro or completely non-technical, MyHub’s cloud-hosted solution offers all the features and functionality you’ll ever need.
We’ve made it so that it’s super simple to set-up (no coding skills or IT experience required) – and is enjoyable to use!
Using simple drag-and-drop functionality, you can create a professional space for your team to start collaborating in minutes! Being cloud-hosted also means you’re future-proofing your investment: you get to benefit from our latest new features and enhancements as soon as they’re released.
Useful Team Collaboration Resources
7 Jotform Alternatives To Consider
Jotform has long been a go‑to online form builder for many businesses, offering a drag-and-drop interface, conditional logic, e-signatures, and thousands of templates. However, common complaints include slow loading times, an outdated editor, and overwhelming template choices—pushing many organizations to explore alternatives.
To help decision-makers, MyHub lists seven compelling Jotform alternatives: forms.app, Zoho Forms, Google Forms, Microsoft Forms, ProProfs Survey Maker, SurveyMonkey, and its own intranet-powered form builder. Each option varies in ease-of-use, feature set, pricing, analytics, and integrations, making it easier to align tool choice with organizational needs and budgets.
MyHub’s form builder stands out by combining intuitive drag-and-drop form design with workflow automation—notifications, approval routing, conditional fields, and role-based permissions—all included at no extra cost within its intranet platform. With built-in integrations to Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, mobile accessibility, and support tools, it offers a more holistic form solution suited for internal processes.
Work From Home Policy – With PDF Sample Template
The widespread shift to home-based work during the pandemic has led organizations to recognize remote and hybrid work as permanent fixtures in modern working life. A formal work-from-home policy is now a necessity—not a luxury—enabling clarity between employer and employee on expectations, rights, and performance standards.
This article outlines the six critical steps in crafting an effective policy: define clear objectives and scope (such as fully remote vs hybrid use), establish eligibility criteria, set communication and work-hour expectations, and specify technical support, equipment provisions, and expense arrangements. It also includes vital sections on cybersecurity protocols, approvals process, and social support to address remote isolation.
By implementing a structured WFH policy, companies can safeguard sensitive data, boost productivity, reduce overhead, and improve employee well-being. Remote workers benefit from greater clarity on equipment allowances, tech support, and workspace setup guidance, while employers protect their interests and strengthen recruitment and retention in an increasingly flexible work landscape.
Extranet vs. Intranet vs. Internet: The Ultimate Explanation
The Internet is an open, global network accessible to anyone, offering unlimited reach but minimal control—making it insecure for sensitive business operations. By contrast, an intranet is a private, internal network owned and managed by a company. Protected with firewalls and login credentials, it offers employees a secure place to communicate, collaborate, and share documents.
An extranet builds on the intranet by granting controlled access to external stakeholders—such as suppliers, partners, or franchisees—enabling collaboration without exposing the entire internal network. It balances openness with privacy, allowing secure sharing of relevant information beyond company walls.
While all three network types use standard web technologies (e.g. HTTP, IP protocols), their main distinctions lie in ownership, user access, and security. The Internet is unregulated and public, the intranet is internal and regulated, and the extranet is a selectively shared private network—each chosen based on organizational collaboration needs and security requirements.
How To Guides – Ideas, Examples, Step by Step
How-to guides are everywhere—and for good reason. They’re simple, step-by-step instructions that help people learn a task or process—whether it’s creating a company onboarding plan or cooking dinner. The best guides are clear, focused, and tailored to their audience, offering actionable steps that actually get results.
These guides serve many purposes: they offer self-service support for customers and employees, boost satisfaction, and reduce repetitive inquiries. Internally, they help onboard new staff, preserve institutional knowledge, and minimize mistakes—especially on common tasks or workflows.
To craft a great how-to guide, start by understanding your audience and researching the task. Then break the process into clear steps using simple, jargon-free language and logical order. Enhance clarity with visuals like images or examples. Finally, wrap up with resource links and a FAQ section for further support.
How To Motivate Employees: 12 Effective Ways
Employee motivation isn’t just about compensation—it’s about engaging the heart and mind. MyHub’s guide lays out four core drivers—recognition, responsibility, advancement, and rewards—which, when embedded in simple workplace strategies, lead to measurable boosts in morale and performance. Notably, 67% of employees cite praise from managers as more motivating than a pay raise.
One practical strategy is recognition. Public acknowledgment—via shout-outs, peer-nominated awards, or spot bonuses—costs little but delivers high impact. Highlighting achievements on the company intranet, newsletters, or team meetings reinforces a culture of gratitude and helps employees feel valued.
Another key approach is empowering employees with responsibility and autonomy. When staff have control over their tasks and decision-making, they become more engaged and committed. Coupled with visible opportunities for professional growth—through training, mentoring or advancement—it helps them see a future with the organisation. A modern intranet can support this by hosting learning modules, skill quizzes, and forums to share expertise.
10 Employee Motivation Strategies That Actually Work
Effective employee motivation extends far beyond pay raises—it’s about purpose, recognition, autonomy, and growth. MyHub’s article highlights that truly motivated teams thrive when they feel valued and empowered, and not just compensated. Strategic motivation taps into company culture and communication to keep employees consistently engaged and productive.
The blog presents 10 practical strategies that consistently motivate employees. These include enhancing one-on-one feedback, setting purpose-driven goals, deploying pulse surveys, launching peer recognition programs, offering remote positive shout-outs, and enabling autonomy through self-service tools on the intranet.
These tactics are designed to be low-cost, scalable, and easy to implement—ideal for managers and HR professionals focused on real change without budget strain. Crucially, these strategies create lasting engagement by reinforcing value, identity, and clear direction. They transform environments where motivation is elective into cultures where it becomes foundational—driving resilience, retention, and performance.






